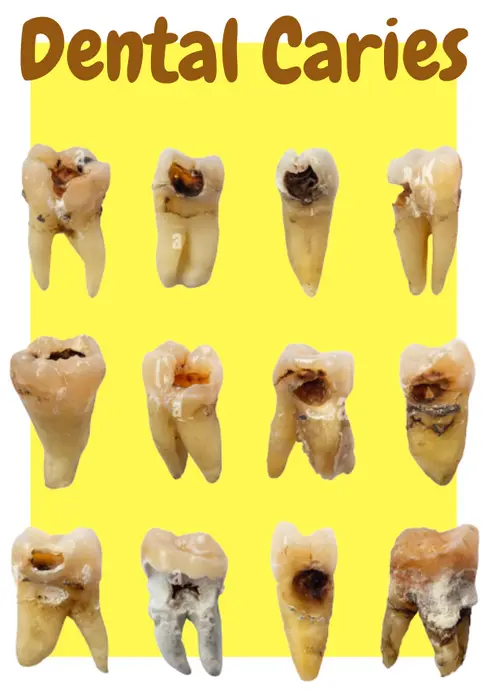
This blog post provides an overview of Dental Caries, including its Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment. It is important to note that regular dental checkups and cleanings, good oral hygiene practices, and a healthy diet are key to preventing and treating dental caries. Additionally, early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent more serious and expensive dental problems down the road. It is always a good idea to consult a dentist or dental professional for personalized advice and treatment plans.
Definition of Dental Caries:
Dental caries is a common oral health problem. Many people call it tooth decay or cavities. It occurs when bacterial plaque and acid erode the enamel and dentin of the teeth. The bacteria produce the acid in the plaque, which feeds on sugars and carbohydrates in the diet. Dental caries can lead to tooth loss, pain, and infection if left untreated.
Prevalence of Dental Caries:
Dental caries is a prevalent oral health issue worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, 60-90% of schoolchildren and nearly 100% of adults have experienced dental caries at some point in their lives. The buildup of plaque on teeth causes a condition containing bacteria. That produces acids that can erode tooth enamel. Elements that can increase the risk of developing dental caries include a diet high in sugar and carbohydrates, poor oral hygiene, and a lack of access to regular dental care. Dental caries can lead to pain, tooth loss, and difficulty eating and speaking if left untreated.
Causes of Dental Caries:
There are several causes for causing this caries. These are described below:
Bacteria in the Mouth:
Dental caries, or cavities, are caused by plaque buildup on teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth, especially in areas where sugar and carbohydrates are present. The plaque contains bacteria that produce acids. This acid can erode tooth enamel and cause cavities.
The most common bacteria associated with dental caries are Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus. These bacteria ferment sugars, such as glucose and fructose, and release lactic acid. The acid can lower the plaque’s pH, leading to the demineralization of the tooth enamel and, in turn, the formation of cavities.
Plaque and Tartar Buildup:
Dental caries, or cavities, are caused by plaque build-up on teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria, food particles, and saliva that forms on teeth. If not removed properly by brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into a substance called tartar. Tartar is more difficult to remove than plaque and can accumulate on teeth, especially along the gum line.
When plaque and tartar build-up on teeth, they breed bacteria. The bacteria in plaque produce acids that can erode tooth enamel and cause cavities. Bacteria that thrive in plaque and tartar can also cause gum inflammation and gum disease.
Plaque and tartar build-up can also lead to the accumulation of harmful bacteria, which can cause bad breath, halitosis, and other oral health problems.
Factors that can increase the risk of plaque and tartar build-up include:
Poor oral hygiene.
A diet high in sugar and carbohydrates.
Dry mouth.
Certain medical conditions and certain medications.
Not visiting the dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups.
Poor Oral Hygiene:
Poor oral hygiene is one of the main causes of dental caries, also known as cavities. When teeth are not properly cleaned, plaque, a film of bacteria, accumulates on the surface of the teeth. These bacteria produce acids that can erode the teeth’ enamel, leading to cavities. Additionally, if plaque is not removed, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. These calculi can also lead to gum disease, damaging the teeth and jawbone. It is important to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly. You also have to visit the dentist for regular checkups and cleanings.
Diet High in Sugar and Carbohydrates:
A diet high in sugar and carbohydrates is another major cause of dental caries. Sugar and carbohydrates are the primary food sources for the bacteria in the mouth. When these foods are consumed in excess, the bacteria in the mouth produce more acids, which can erode the teeth’ enamel and lead to cavities. Additionally, consuming sugary and carb-heavy foods and drinks frequently, especially between meals, can increase the chances of developing cavities. The longer sugary and carb-heavy foods stay in the mouth, the more time bacteria have to ferment and produce acid, which can dissolve the enamel on the teeth. Limiting sugary and carb-heavy foods and drinks is important to prevent dental caries. It will help if you practice good oral hygiene, also.
Genetic and Systemic Factors:
Genetic and systemic factors can also contribute to the development of dental caries. Some people may be genetically predisposed to having weaker teeth or a dry mouth. And dry mouth can increase their risk of cavities. A dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, can occur due to medications, medical conditions, or other factors and can decrease saliva production. Saliva helps to neutralize acids and wash away food particles, so a decrease in saliva can lead to an increase in plaque and acid buildup.
Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, which can affect the body’s ability to fight off infections, can increase the risk of developing dental caries. Individuals with an eating disorder may develop cavities because they may not have enough nutrients to support healthy teeth and gums.
It’s important to note that while some of these factors may increase the risk of dental caries, they can be managed or treated with good oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, and by following a healthy diet.
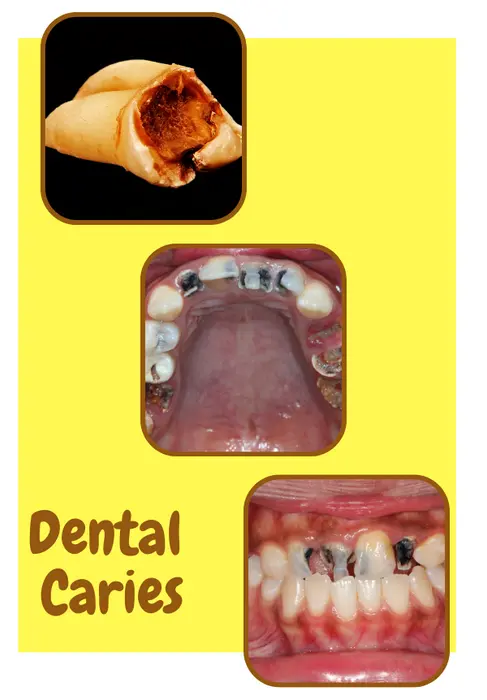
Symptoms of Dental Caries:
Dental caries, also known as cavities, can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
Tooth Sensitivity:
As cavities develop, they can cause the tooth’s nerve to become more sensitive to temperature changes and sweet, sour, and spicy foods.
Pain or Discomfort When Biting or Chewing:
When the cavities are large enough, they can cause pain or discomfort when biting or chewing. This pain or discomfort is often a sign of a more advanced cavity.
Visible Holes or Pits in the Teeth:
As the tooth’s enamel is eroded by acid, it can leave visible holes or pits in the teeth. These holes or pits can be seen as a dark spots on the tooth.
Discoloration of the Teeth:
As cavities develop, they can cause the tooth to discolor, appearing as a yellow or brown spot.
Bad Breath:
Bacteria that cause cavities can also produce a bad odor in the mouth, leading to bad breath.
It’s important to note that cavities may not cause any symptoms in the early stages, so regular dental check-ups are important to detect them early. It’s also important to practice good oral hygiene and limit sugary and carb-heavy foods and drinks to prevent the development of cavities.
Prevention and Treatment of Dental Caries:
Preventing and Treating Dental Caries involves good oral hygiene practices, a healthy diet, and regular dental check-ups and treatments. Some of the ways to prevent and treat dental caries include:
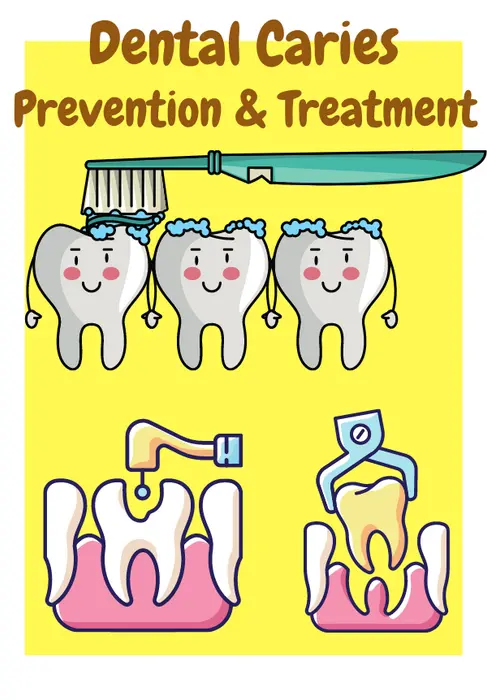
Good oral hygiene practices:
Brushing and flossing are essential for removing plaque and bacteria from the teeth. These brushing and flossing can help prevent cavities.
Limiting sugary and starchy foods:
Consuming sugary and starchy foods in excess can increase the risk of cavities. Limiting these foods and practicing good oral hygiene can help prevent cavities.
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings:
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings can help detect cavities early and remove plaque and tartar buildup.
Fluoride treatments and sealants:
Fluoride is a mineral that can strengthen tooth enamel and make it more resistant to decay. Sealants are a thin coating applied to the teeth’ surface, especially the molars, to protect them from decay.
Fillings, root canals, and extractions:
If a cavity has progressed to a more advanced stage, a filling may require to repair the tooth. Sometimes, a root canal may require removing the infected pulp inside the tooth. An extraction may be necessary to remove a badly decayed tooth in severe cases.
It’s important to note that early treatment of cavities can prevent them from progressing to more severe stages, which can lead to more invasive and expensive treatments. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, and a healthy diet are key to preventing and treating dental caries.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, dental caries, also known as cavities, are common dental problems caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth. They are caused by various factors, including poor oral hygiene, a diet high in sugar and carbohydrates, and genetic and systemic factors. Symptoms of dental caries can include tooth sensitivity, pain or discomfort when biting or chewing, visible holes or pits in the teeth, discoloration, and bad breath.
Preventing and treating dental caries involves a combination of good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing regularly, limiting sugary and starchy foods, regular dental check-ups and cleanings, fluoride treatments and sealants, fillings, root canals, and extractions. Early treatment of cavities can prevent them from progressing to more severe stages, leading to more invasive and expensive treatments.
It’s important to note that regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, and a healthy diet are key to preventing and treating dental caries. Taking care of your oral health can help keep your teeth and gums healthy and reduce your risk of developing cavities.
Reference:
1. National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research
2. American Dental Association
Leave a Reply